Redis - Replication
Redis - Replication
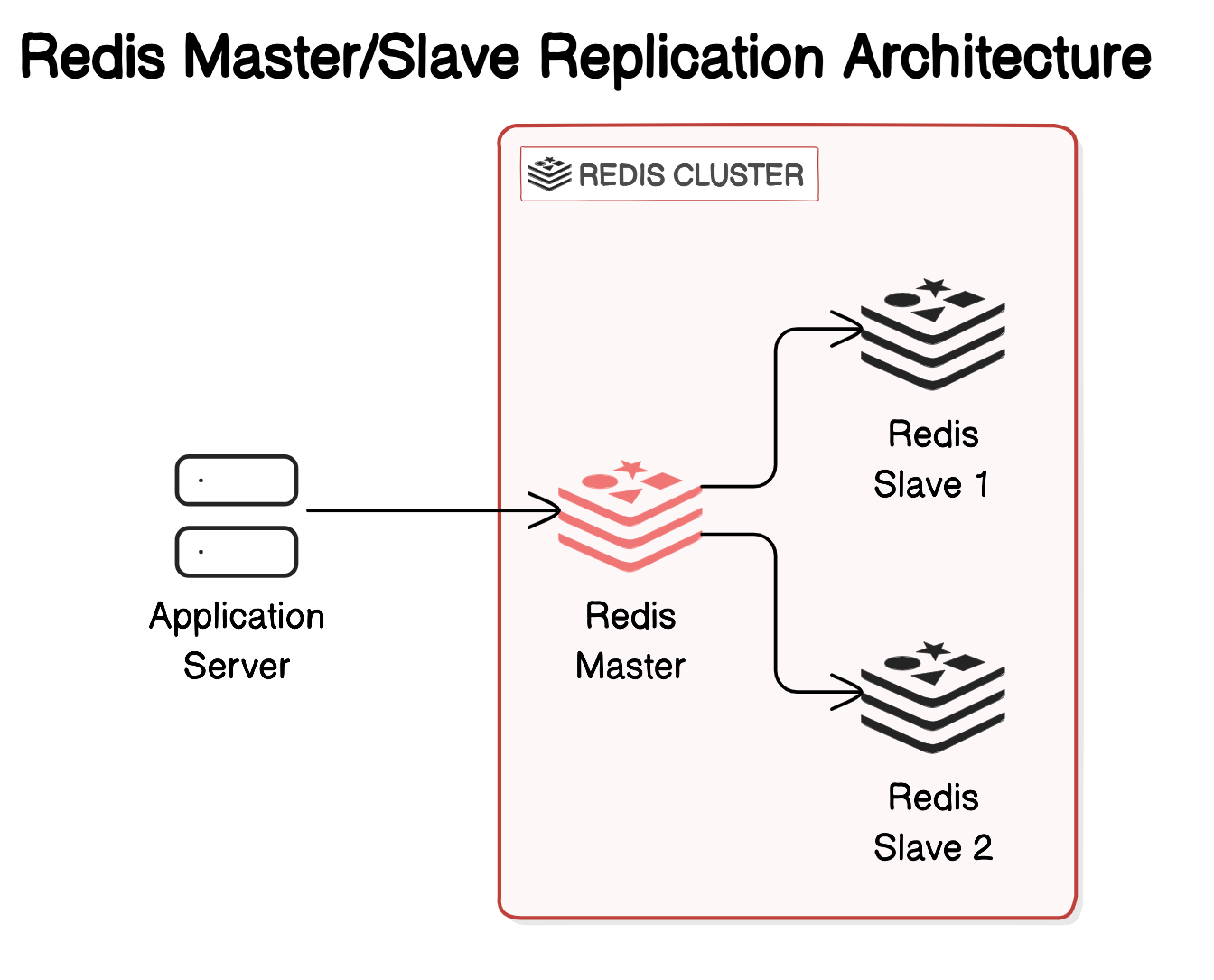
Redis Replication
Redis Replication
Key Facts
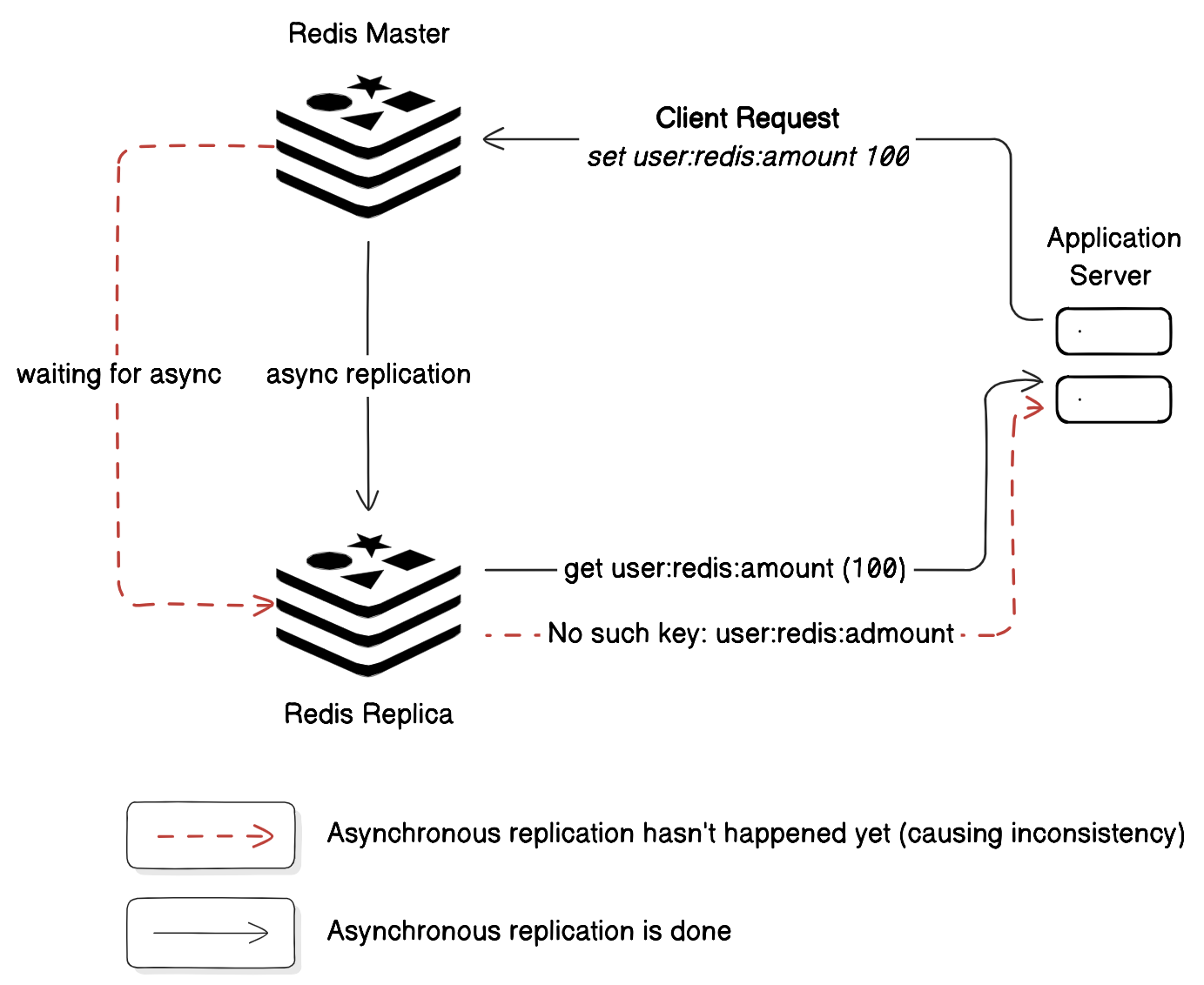
- Replication is Asynchronous
- When a client writes data to the main Redis server (called the Master), the data is copied to other Redis servers (called Replicas).
- However, this replication happens asynchronously—meaning the client doesn’t control when the data reaches the replica.
- Non-blocking Replication on Master
- Replication doesn’t slow down the Master server for clients. Redis Master continues to respond to clients while sending data to replicas.
- Occasional Blocking on Replica
- Sometimes, a replica might be syncing data from the Master and won’t respond to client requests until it’s up-to-date.
- Flexible Number of Replicas
- A Redis Master can have as many replicas as needed for distributing data.
- Replicas are Usually Read-Only
- By default, replicas only respond to read requests.
- You can allow write requests on replicas, but changes made this way are only temporary; they’ll be overwritten when the Master syncs with the replica again.
- Replica as a Master
- A replica can act as a Master to other replicas, creating a chain of replication if needed.
Why Use Replication?
- High Availability: Replicas provide backups of data, helping keep data accessible even if one server fails.
- Read Load Distribution: Multiple replicas can handle read requests, balancing the load.
Alternative to Persistence: Replication can provide data reliability even if persistence (writing to disk) is not configured.
Types of Replication
1. Full Sync
- When a new replica joins, it needs all the data from the Master. This is called Full Sync.
- How Full Sync Works:
- Redis Master forks (creates a separate process) to copy all data to the replica, which lets the Master keep responding to clients.
- Two Methods for Data Transfer:
- Disk-based: The Master saves data to disk and sends the file to the replica (older method).
- Diskless: The Master sends data directly to the replica without saving to disk.
- When Full Sync Happens:
- Setting up a new replica
- When a replica falls too far behind in syncing with the Master
2. Partial Sync
- In cases where only a small amount of data needs syncing, Partial Sync updates replicas with recent changes instead of copying everything.
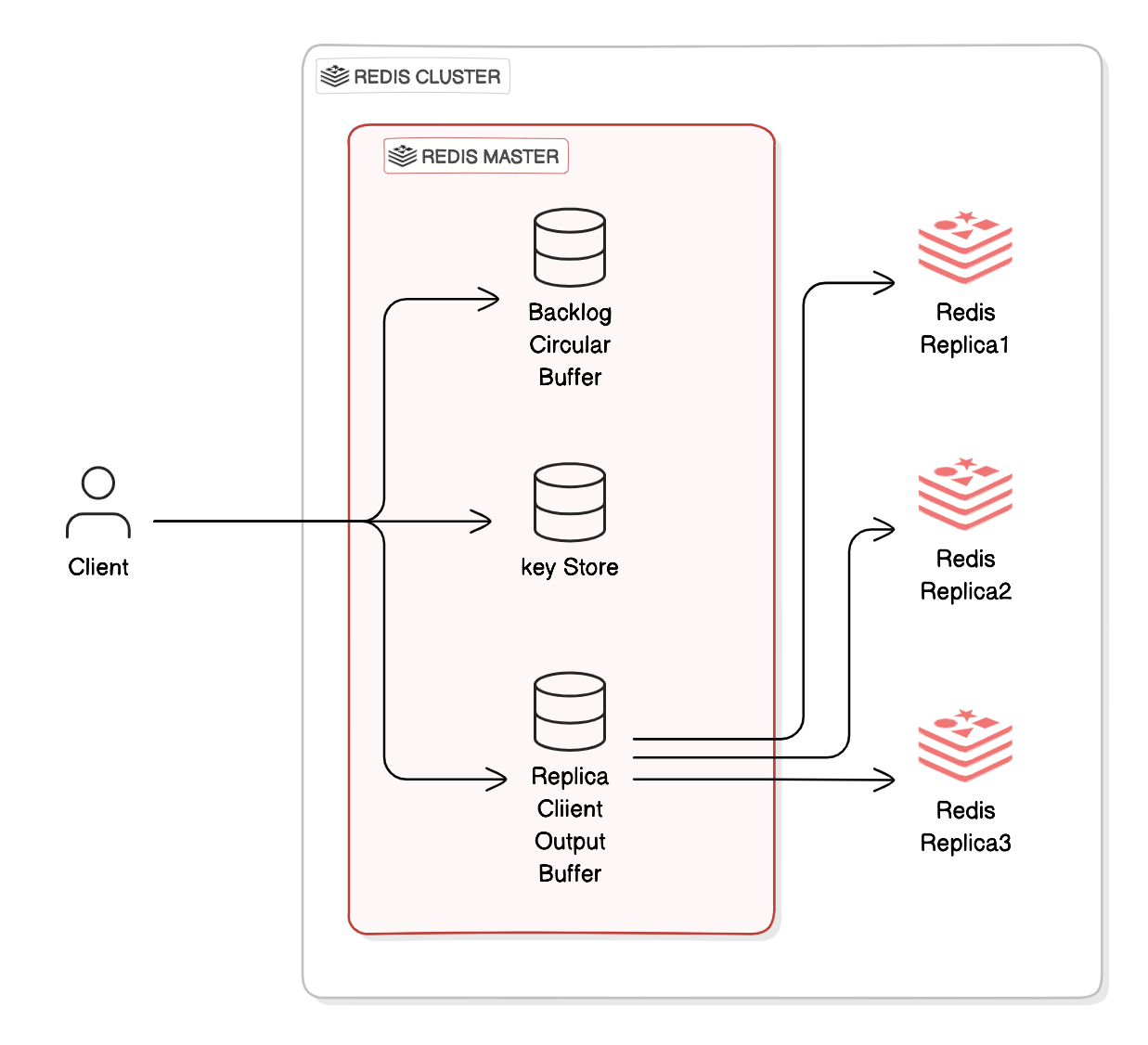
- Key Components:
- Replication Backlog: A limited-size memory buffer where recent writes are stored.
- Replication ID: Each server gets a unique ID on restart, helping to manage syncs.
- Replication Offset: Keeps track of the exact position of each update in the backlog.
- Replica Client Output Buffer: Stores data that the Master sends to each replica.
Important Replication Configurations
replicaof <master_ip> <master_port>- Connects a Redis instance to a Master as a replica.
Example:
1 2 3
replicaof localhost 7001 # Connect to a Master on localhost at port 7001 replicaof NO ONE # Disconnects from Master
repl-backlog-size <size>- Sets the size of the replication backlog buffer (e.g.,
1mb).
- Sets the size of the replication backlog buffer (e.g.,
repl-timeout <seconds>- Sets a time limit for replicas to wait for data from the Master before timing out (e.g.,
60seconds).
- Sets a time limit for replicas to wait for data from the Master before timing out (e.g.,
client-output-buffer-limit replica <hard limit> <soft limit> <time>- Configures limits for each replica’s output buffer. Exceeding this can cause disconnection.
Consistency in Redis
Redis doesn’t guarantee 100% consistency but offers settings to reduce inconsistency risk:
- Read-Only from Master
- By reading only from the Master, clients get the most accurate data.
- Server Settings for Consistency
min-replicas-to-writeandmin-replicas-max-lag: This two config option goes hand-in-hand, i.e., ifmin-replicas-to-writethat has a lag fewer thanmin-replicas-max-lagthen accept the write.
- Client Option for Consistency
WAIT <num-replicas> <timeout-millis>: Ensures a certain number of replicas receive data before the command completes.
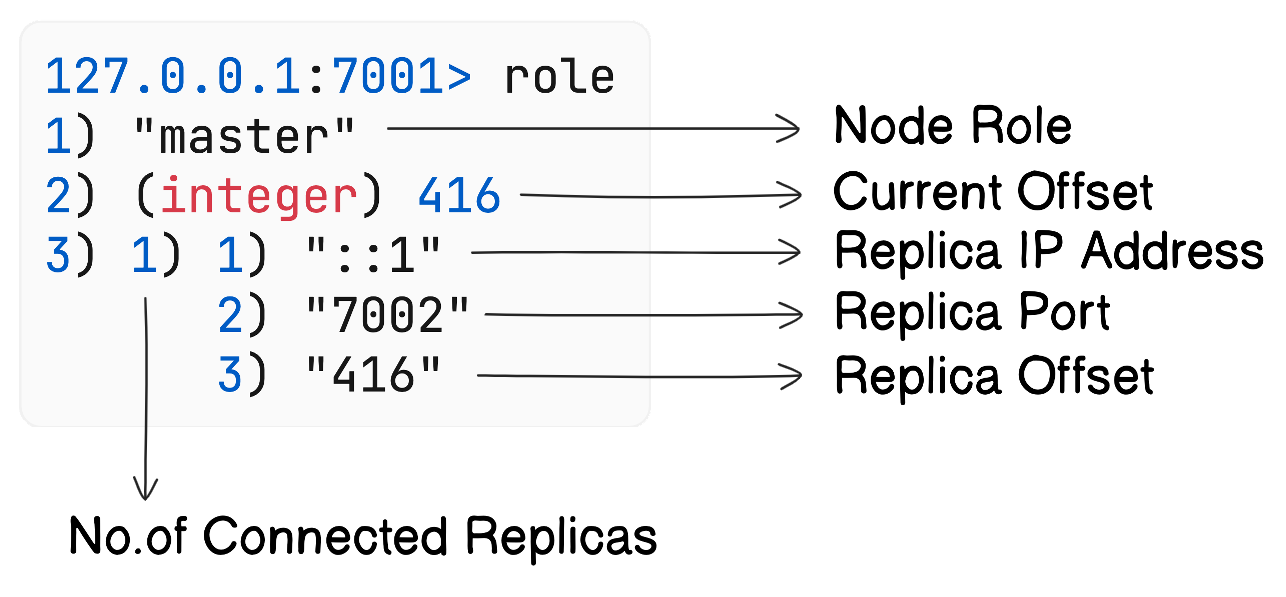
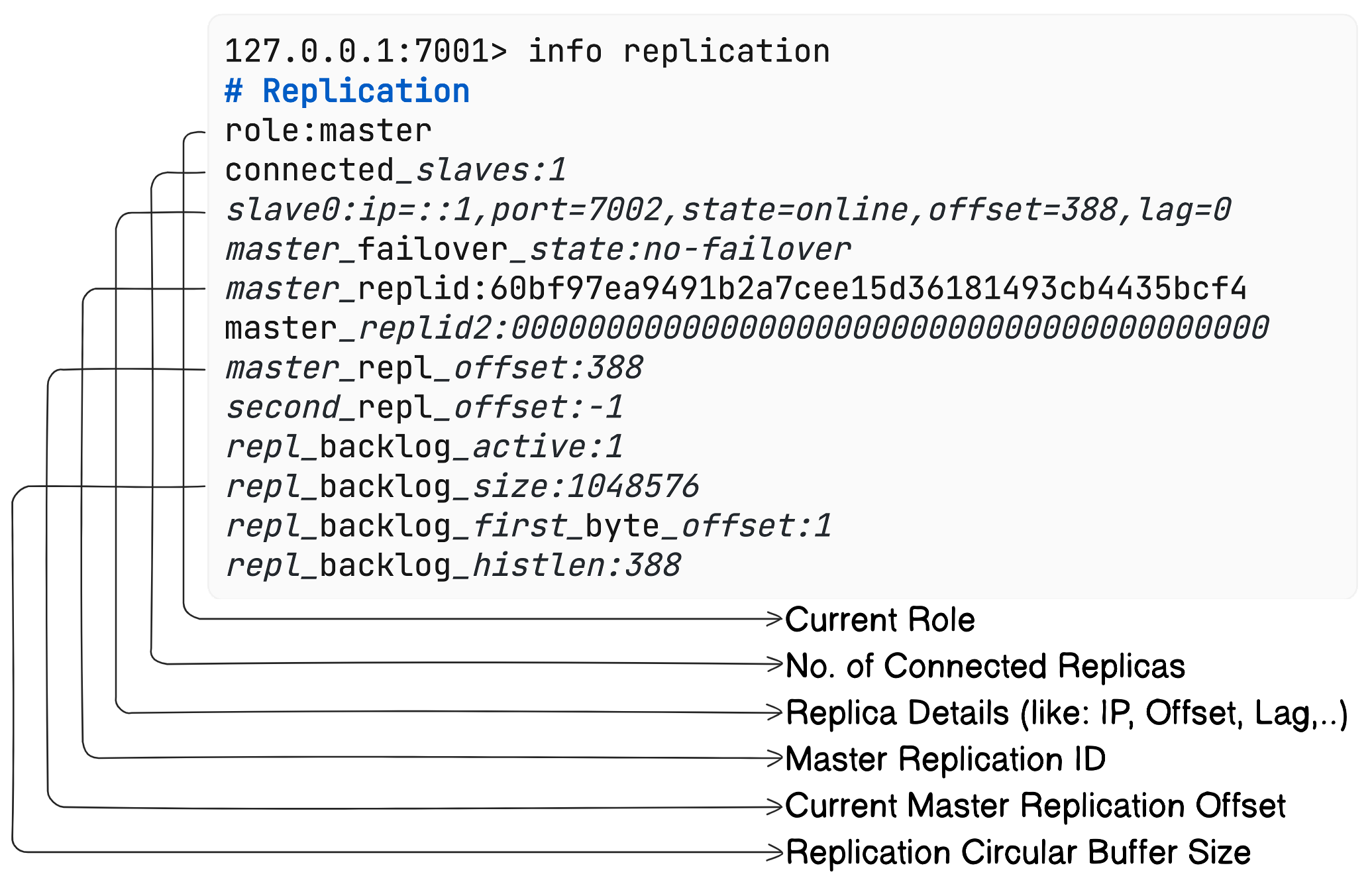
Replication Monitoring
role
info replication
Memory Usage Considerations
- Replication Backlog:
- Shared buffer for all replicas, reducing available memory for user data.
- Replica Client Output Buffer:
- Each replica has its buffer, with limits to control memory usage.
Common Replication Issues & Fixes
- Out-of-Memory for Full Sync:
If a Full Sync fails due to lack of memory, allow Redis to allocate more memory with:
1 2
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
- Timeout on Replica During Full Sync:
- Increase
repl-timeoutif replicas disconnect during Full Sync.
- Increase
- Output Buffer Limit Exceeded:
- If the output buffer overflows, increase the
client-output-buffer-limit replicasetting to avoid disconnection.
- If the output buffer overflows, increase the
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.