Memcached - Part-2
Memcached - Part 2
How Memcached works?
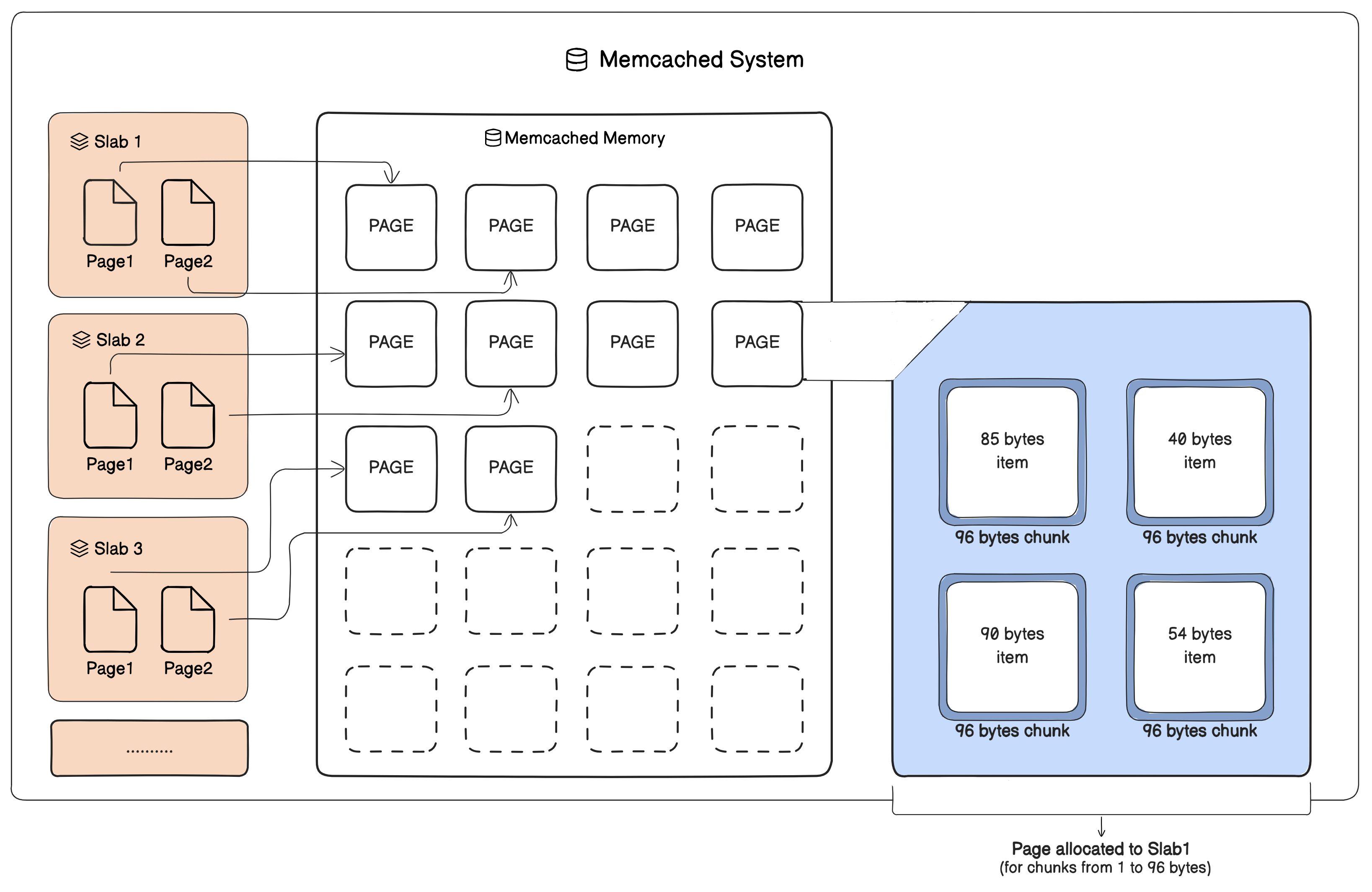
- Memcached organizes its memory into slabs, which are groups of objects with similar sizes. This helps prevent memory waste caused by fragmentation. For example:
- The first slab holds items up to 96 bytes.
- The second slab holds items from 96 to 120 bytes, and so on.
- The largest slab holds items between 753.1 KB and 1 MB (the maximum size).
- The size of each slab increases by 25% (default) compared to the previous one and is rounded to the nearest multiple of 8.
- A page is a 1 MB block of memory used to store items. Each slab gets one or more pages, depending on the total memory allocated for Memcached (set using the
-moption). The pages are divided into chunks. - A chunk is the smallest unit of memory in a slab. For example:
- A slab for items up to 96 bytes will assign 96 bytes to every item, even if the actual data is smaller (e.g., the string “hi” still uses 96 bytes).This wastes a little memory but makes updates faster because items stay in fixed-size chunks.
What is memcached-tool ?
memcached-tool is a command-line utility used by administrators and developers to:
- Inspect Memory Usage:
- It provides a breakdown of how memory is allocated to different slabs.
- View Key Metadata:
- Helps list and analyze keys stored in Memcached, including their sizes and slab assignments.
- Monitor Statistics:
- Displays performance and configuration metrics.
- Debugging and Diagnostics:
- Helps in identifying memory inefficiencies or potential bottlenecks in your Memcached deployment.
Download the memcached-tool script directly from Github
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
❯ curl -sSLO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/memcached/memcached/master/scripts/memcached-tool && chmod +x memcached-tool
❯ ./memcached-tool
Usage: memcached-tool <host[:port] | /path/to/socket> [mode]
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 display # shows slabs
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 # same. (default is display)
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 stats # shows general stats
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 settings # shows settings stats
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 sizes # shows sizes stats
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 dump [limit] # dumps keys and values
memcached-tool 10.0.0.5:11211 keys [-u] [limit] # dumps keys (-u: unescape special characters)
...
Modes in memcached-tool
The memcached-tool utility has different modes, including display and keys, which are explained below.
displayModeThis is the default mode of
memcached-tooland is used to show how memory is allocated across different slabs. Slabs in Memcached are pre-allocated memory chunks that store items of similar size to minimize fragmentation.1 2 3 4 5
❯ ./memcached-tool localhost:11211 # Item_Size Max_age Pages Count Full? Evicted Evict_Time OOM 1 96B 0s 1 0 no 0 0 0 2 120B 2305261s 1 1034 no 0 0 0 3 152B 2990s 1 4 no 0 0 0Fields Explained:
Field Description #Slab ID Item_SizeThe size of items stored in this slab Max_ageThe age of the oldest item in this slab (in seconds) PagesNumber of 1 MB memory pages assigned to this slab CountNumber of items currently stored in this slab Full?Indicates if the slab is full EvictedNumber of items evicted from this slab due to memory constraints Evict_TimeThe age of the most recently evicted item (in seconds) OOMNumber of “Out of Memory” errors caused when trying to allocate new items Use Cases:
This mode is great for understanding how Memcached is using memory and diagnosing issues like high eviction rates or memory pressure.
keysModeThe
keysmode inmemcached-toollists detailed metadata about keys stored in Memcached. This is useful for inspecting cache contents and debugging issues related to key storage.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
❯ ./memcached-tool memcached-rpg:11211 keys 5 Dumping memcache keys key=72a87a54e7 exp=1736770574 la=1734092173 cas=137868 fetch=yes cls=2 size=103 flags=4 key=8c5104ebc8 exp=1735230851 la=1732552472 cas=28037 fetch=yes cls=2 size=110 flags=4 key=a5caebb472 exp=1734816324 la=1732137924 cas=187 fetch=no cls=2 size=103 flags=4 key=MemcachedNotificationCounterad357cd7524f7469total exp=1734443795 la=1734440195 cas=161314 fetch=no cls=3 size=125 flags=0 key=88ac444fbe exp=1736770964 la=1734092564 cas=137897 fetch=no cls=2 size=103 flags=4 ...
Fields Explained:
Field Value Description key<key_name>The name of the key stored in Memcached exp<expiration_timestamp>The expiration time of the key, represented as a Unix timestamp. If the key has no expiration, this value is 0la<last_access_timestamp>The timestamp (Unix time) of the last time this key was accessed cas<cas_id>The Check and Set (CAS) ID associated with this key fetch<yes\|no>Indicates whether the key has been fetched since it was added to the cache: yes: The key has been accessed after being addedno: The key has not been accessed yetcls<slab_class_id>The slab class where this key is stored size<value_size>The size (in bytes) of the value associated with this key flags<flags_value>A user-defined 32-bit integer that can store additional metadata with the key